Understanding and Preventing Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Cancer is a group of diseases distinguished by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells. If not detected and treated early, it can result in severe illness and death. Understanding cancer’s causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies is critical for reducing its impact on individuals and society. This article provides a comprehensive overview of cancer, including its common types, risk factors, prevention strategies, and the importance of early detection.
What is Cancer?
Cancer is not a single disease but a collection of related diseases. It can develop in almost any part of the body, when cells grow uncontrollably, forming tumors. Tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant tumors invade nearby tissues and can spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems. Cancer is a large group of diseases that can start in almost any organ or tissue of the body when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably, go beyond their usual boundaries to invade adjoining parts of the body and/or spread to other organs.
Common Types of Cancer
Understanding the various types of cancer is essential for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment. Here are some of the most common types:
- Breast Cancer:
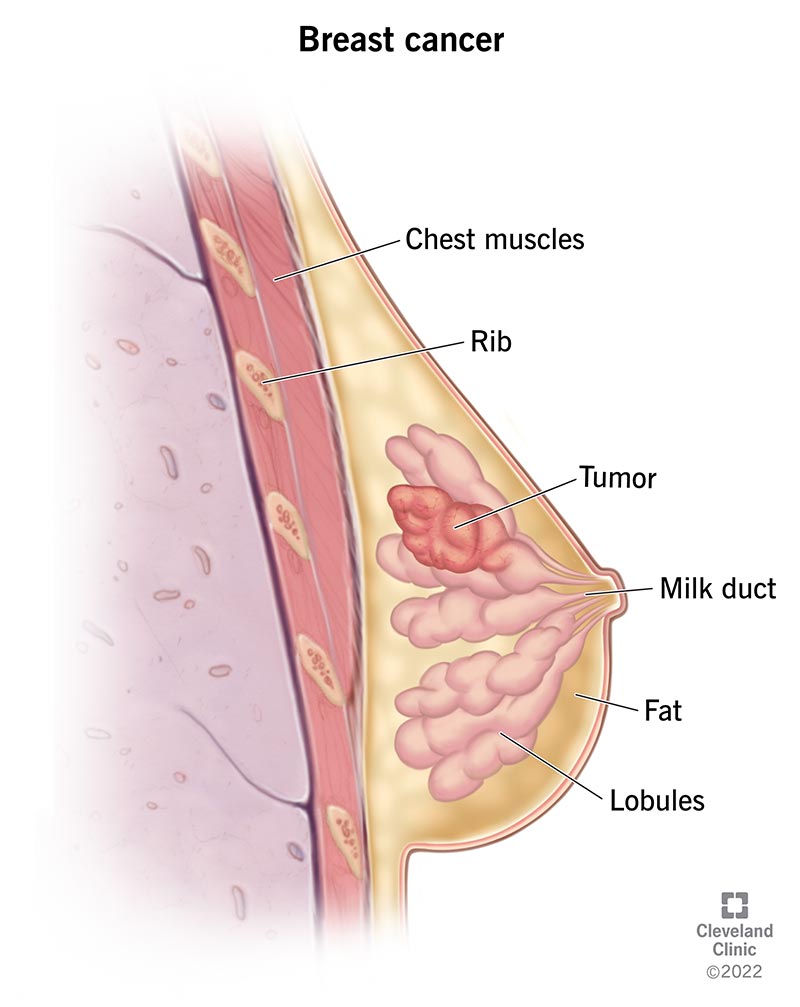
- One of the most common cancers in women, breast cancer originates in the breast tissues, typically in the ducts or lobules.
- Symptoms: Lump in the breast, changes in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, and nipple discharge.
2. Lung Cancer:
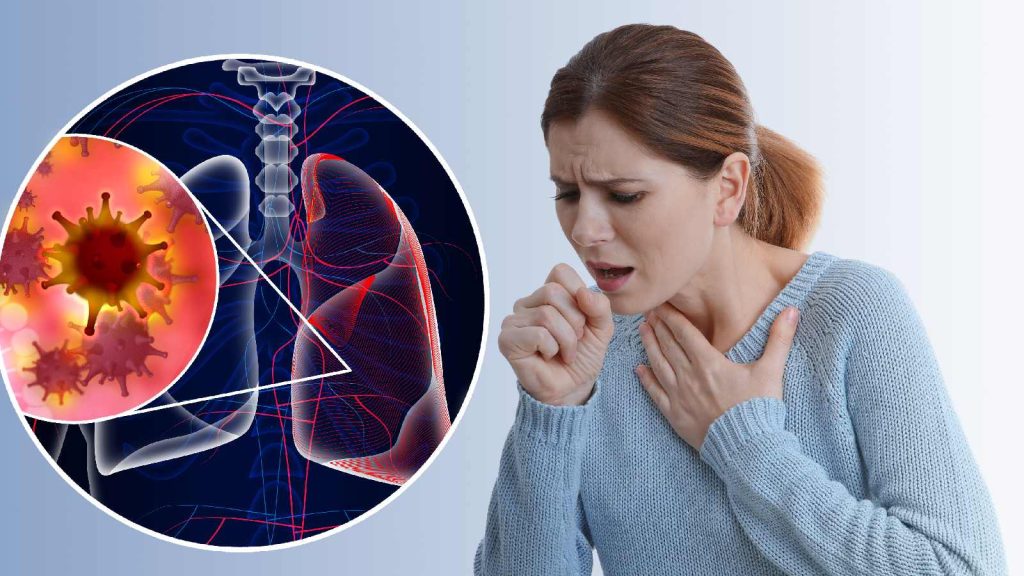
- Often associated with smoking, lung cancer can also affect non-smokers.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and coughing up blood.
3. Prostate Cancer:
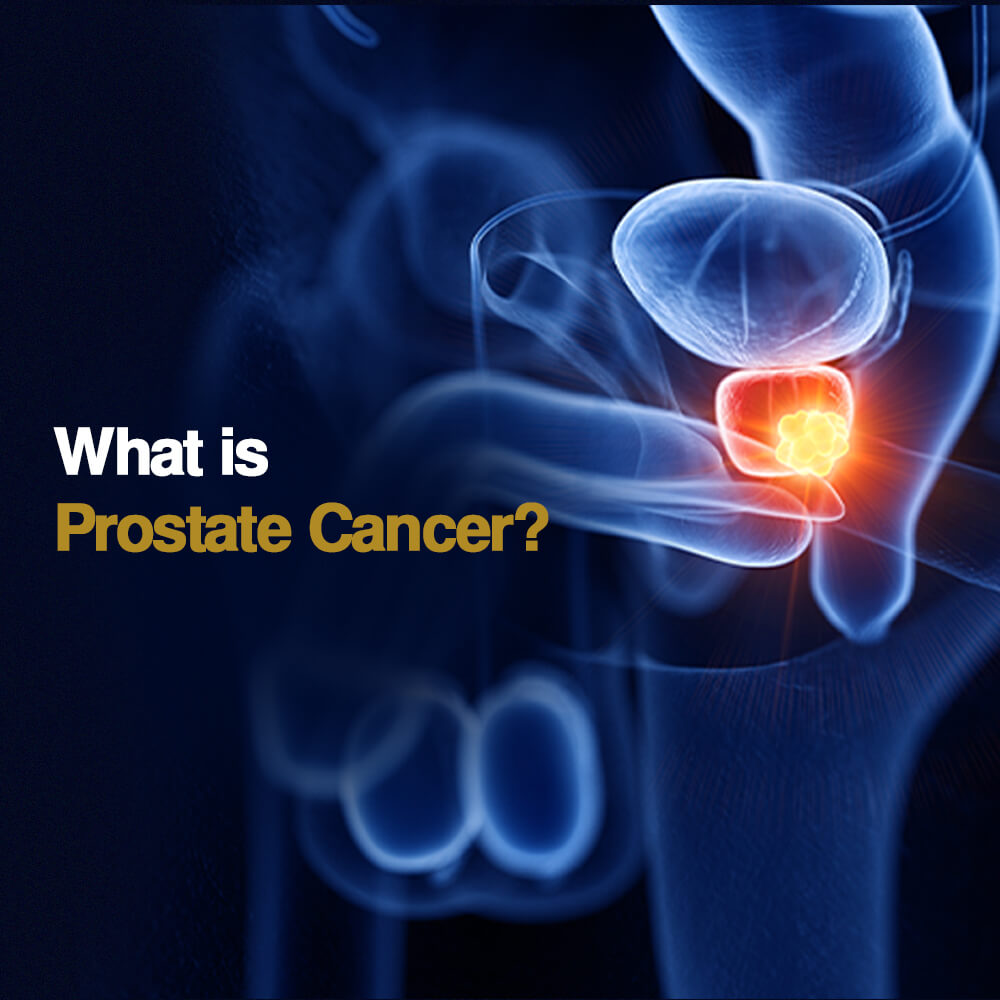
- Common in older men, prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland.
- Symptoms: Difficulty urinating, weak urine flow, and blood in the urine or semen.
4. Colorectal Cancer:
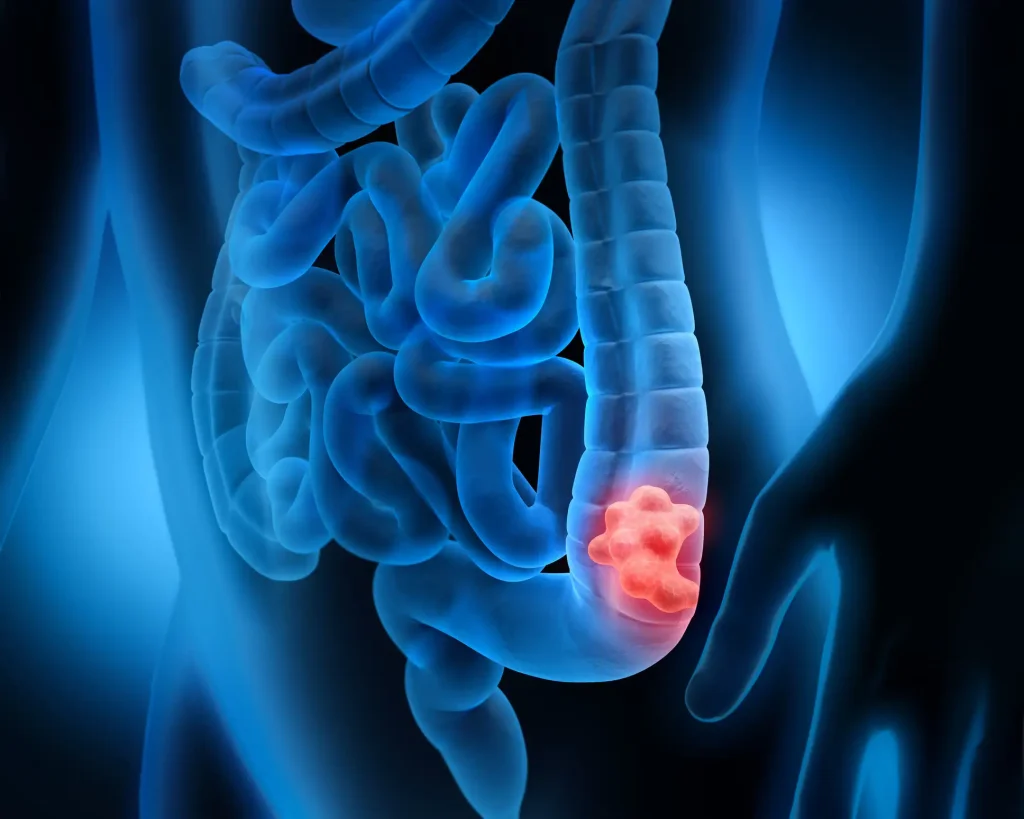
- This cancer affects the colon or rectum and is often detected through screening tests.
- Symptoms: Changes in bowel habits, blood in the stool, and abdominal discomfort.
5. Skin Cancer:
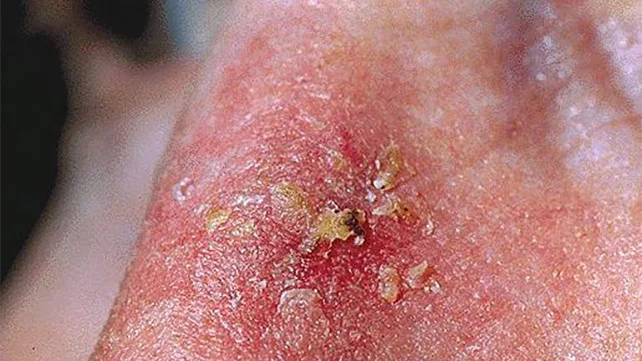
- Includes melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancers, usually caused by excessive sun exposure.
- Symptoms: New or changing moles, skin lesions, and sores that do not heal.
6. Liver Cancer:
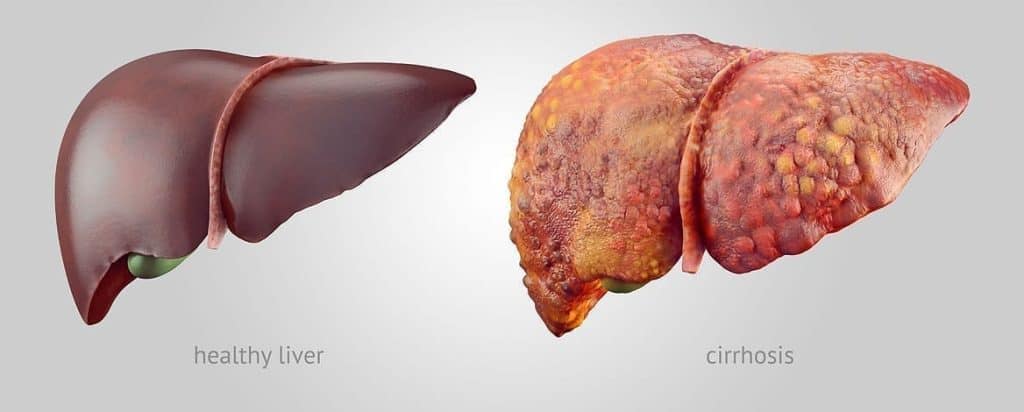
- Often linked to chronic liver diseases such as hepatitis and cirrhosis.
- Symptoms: Weight loss, loss of appetite, upper abdominal pain, and jaundice.
7. Pancreatic Cancer:
- Known for its poor prognosis, pancreatic cancer is often detected late.
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, weight loss, jaundice, and digestive problems.
8. Leukemia:
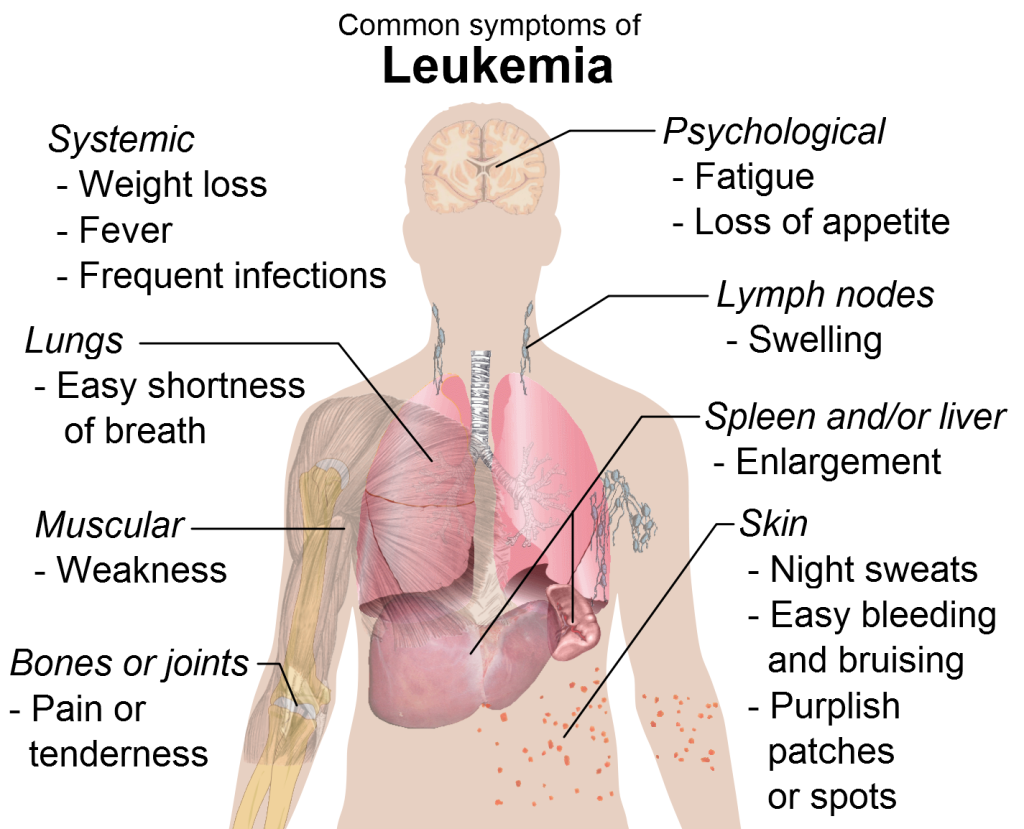
- A cancer of the blood and bone marrow, affecting white blood cells.
- Symptoms: Fatigue, frequent infections, easy bruising, and bleeding.
Risk Factors and Causes
Understanding the risk factors for cancer can help in taking preventive measures. While some risk factors are beyond control, such as genetics, many can be managed through lifestyle choices. Key risk factors include:
- Tobacco Use:
- Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer and contributes to other cancers such as mouth, throat, and bladder cancer.
- Diet and Physical Activity:
- Poor diet, obesity, and lack of physical activity are linked to several cancers, including breast, colorectal, and endometrial cancer.
- Sun Exposure:
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun and tanning beds increases the risk of skin cancer.
- Alcohol Consumption:
- Heavy alcohol use is associated with an increased risk of cancers of the mouth, throat, esophagus, liver, and breast.
- Environmental Exposure:
- Exposure to certain chemicals and pollutants can increase cancer risk. Examples include asbestos, benzene, and radon.
- Infections:
- Certain infections, such as human papillomavirus (HPV), hepatitis B and C, and Helicobacter pylori, can lead to cancer.
- Genetics:
- Family history and inherited genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can significantly increase cancer risk.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing cancer involves a combination of lifestyle changes, vaccinations, and regular screenings. Here are some effective strategies:
- Avoid Tobacco:
- The most significant step to reduce cancer risk is to avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke.
- Healthy Diet:
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit processed foods, red meats, and sugary beverages.
- Regular Exercise:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through diet and exercise to reduce the risk of several cancers.
- Protect Your Skin:
- Use sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, wear protective clothing, and avoid tanning beds.
- Limit Alcohol:
- If you choose to drink, do so in moderation. Limit to one drink per day for women and two for men.
- Vaccinations:
- Vaccinate against cancer-causing infections such as HPV and hepatitis B.
- Regular Screenings:
- Participate in recommended cancer screenings, such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and Pap smears. Early detection increases the chances of successful treatment.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of cancer can significantly improve the chances of successful treatment and survival. Regular screenings and being aware of the symptoms can lead to early diagnosis. Here are some common screening tests:
- Mammograms:
- Recommended for women aged 40 and above for early detection of breast cancer.
- Colonoscopy:
- Recommended for adults aged 50 and above for detecting colorectal cancer and polyps.
- Pap Smear and HPV Test:
- Recommended for women aged 21 to 65 for detecting cervical cancer and precancerous changes.
- Low-Dose CT Scan:
- Recommended for heavy smokers and former smokers aged 55 to 74 for early detection of lung cancer.
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test:
- Recommended for men aged 50 and above for detecting prostate cancer.
Advances in Cancer Research and Treatment
Significant progress has been made in cancer research, leading to improved treatments and survival rates. Some notable advances include:
- Targeted Therapy:
- Drugs that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression, such as HER2 in breast cancer.
- Immunotherapy:
- Treatments that boost the body’s immune system to fight cancer, such as checkpoint inhibitors and CAR T-cell therapy.
- Personalized Medicine:
- Tailoring treatment based on the genetic profile of the patient’s cancer, leading to more effective and less toxic therapies.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery:
- Techniques such as laparoscopy and robotic surgery offer less invasive options for cancer surgery with faster recovery times.
- Advances in Radiation Therapy:
- Improved precision in targeting tumors with radiation, reducing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Coping with a Cancer Diagnosis
A cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming and emotionally challenging. Here are some tips for coping:
- Seek Support:
- Reach out to family, friends, and support groups for emotional and practical support.
- Educate Yourself:
- Learn about your specific type of cancer and treatment options to make informed decisions.
- Communicate with Your Healthcare Team:
- Maintain open communication with your doctors and ask questions about your diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis.
- Take Care of Your Mental Health:
- Consider counseling or therapy to help manage anxiety, depression, and other emotional challenges.
- Stay Active:
- Engage in physical activities as recommended by your healthcare team to maintain your strength and energy.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet:
- Eat a balanced diet to support your body during treatment and recovery.
Cancer is a complex and multifaceted disease, but understanding its causes, risk factors, and prevention strategies can empower individuals to take proactive steps in reducing their risk. By making healthy lifestyle choices, participating in regular screenings, and staying informed about the latest advances in cancer research and treatment, we can work towards a future with lower cancer incidence and improved outcomes for those affected by this disease. Remember, early detection is key, so be vigilant about monitoring your health and seeking medical advice when needed.