Infertility: Understanding, Causes, and Treatments
Infertility is a common issue that affects millions of couples worldwide. It can be a demanding and emotional journey, but understanding its causes and the available treatments can help those affected cross this difficult period. This article focuses on providing a comprehensive overview of infertility, its causes, and the latest treatments available.
Understanding Infertility
Infertility is typically defined as the incapability to conceive after one year of regular, unprotected intercourse. Infertility is a diseases of the male or female reproductive system defined by the failure to achieve a pregnancy after 12 months or more of unprotected sexual intercourse. Infertility may occur due to male, female or unexplained factors. For women over the age of 35, this period is reduced to six months. Infertility can affect both men and women and may result from a variety of factors, including genetic, environmental, and lifestyle influences.
Types of Infertility
- Primary Infertility: This refers to couples who have never been able to conceive.
- Secondary Infertility: This occurs when couples who have previously conceived and had a child are unable to conceive again.
Causes of Infertility
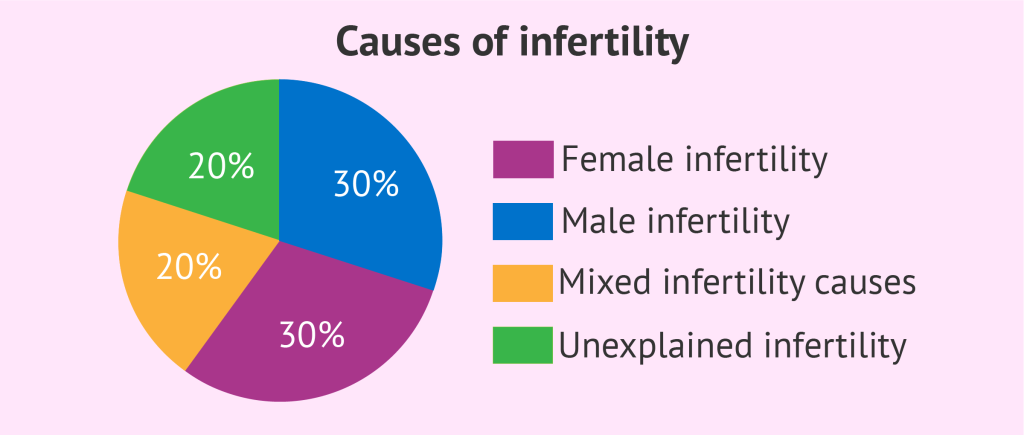
Infertility can be due to issues in either partner or a combination of factors. The causes can be broadly categorized into male and female infertility.
Female Infertility
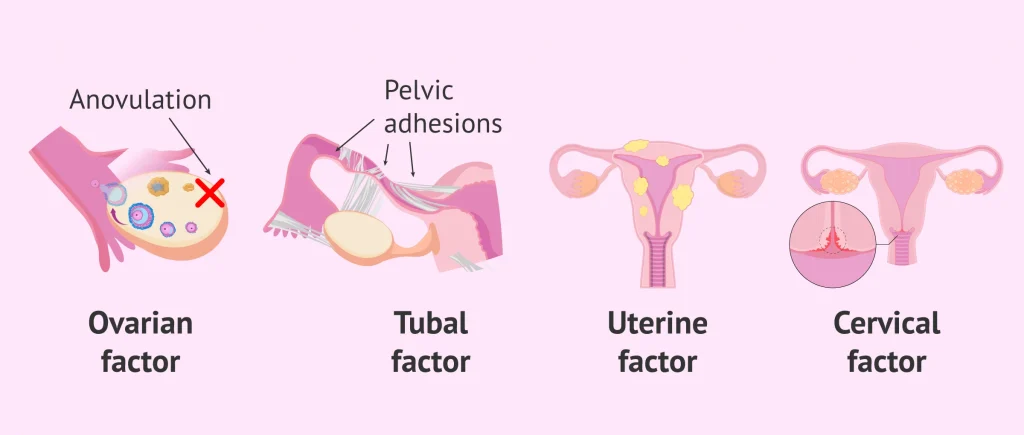
- Ovulation Disorders: Problems with ovulation account for most cases of female infertility. Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), hypothalamic dysfunction, and premature ovarian insufficiency can interfere with the regular release of eggs.
- Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage: This can be caused by pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, or previous surgeries.
- Endometriosis: This condition occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus, causing inflammation and scarring, which can interfere with conception.
- Uterine or Cervical Abnormalities: Issues like fibroids, polyps, or structural abnormalities in the uterus or cervix can impede the implantation of a fertilized egg or increase the risk of miscarriage.
- Age: Female fertility declines with age, significantly after the age of 35.
Male Infertility
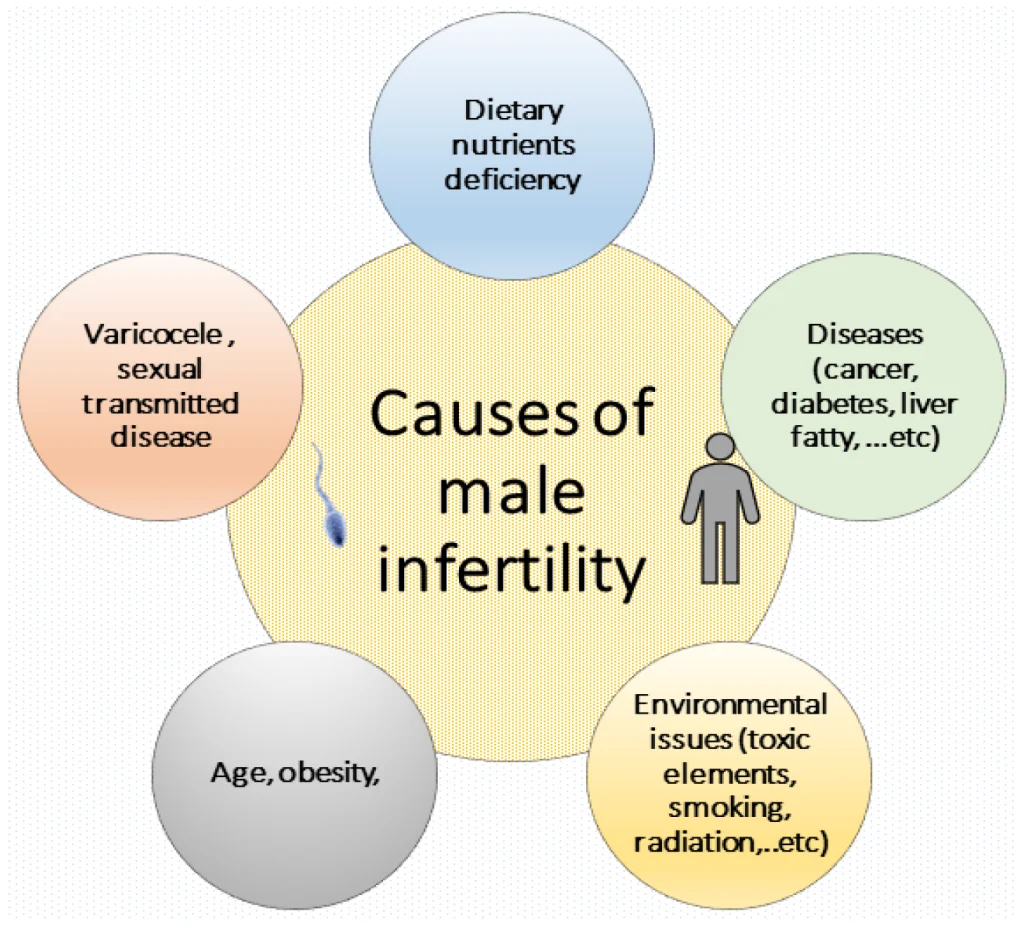
- Sperm Disorders: Problems with the production or function of sperm, such as low sperm count, poor motility, or abnormal shape, are common causes of male infertility.
- Testicular Issues: Conditions like varicocele, infections, trauma, or undescended testicles can impact sperm production and quality.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Disorders affecting the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, or testicles can disrupt the production of hormones necessary for sperm production.
- Genetic Disorders: Genetic conditions such as Klinefelter syndrome can affect sperm production and quality.
- Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, and exposure to environmental toxins can negatively impact sperm health.
Diagnosing Infertility
Diagnosing infertility typically involves a series of tests and evaluations for both partners. These may include:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: A detailed medical history and physical examination can help identify potential causes of infertility.
- Ovulation Testing: Women can use over-the-counter ovulation kits or undergo blood tests to confirm if they are ovulating regularly.
- Hormone Testing: Blood tests can measure hormone levels that regulate reproduction in both men and women.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, hysterosalpingography (HSG), and laparoscopy can help identify structural abnormalities or blockages in the reproductive organs.
- Semen Analysis: This test evaluates the quantity and quality of a man’s sperm.
- Genetic Testing: Genetic tests can identify underlying genetic causes of infertility in both men and women.
Treatments for Infertility
The treatment of infertility depends on the underlying cause, the age of the partners, and the duration of infertility. Here are some common treatments:
Medications
- Ovulation Induction: Medications such as clomiphene citrate and letrozole can stimulate ovulation in women with ovulation disorders.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormonal treatments can help regulate or stimulate ovulation in women and improve sperm production in men.
Surgical Treatments
- Laparoscopy and Hysteroscopy: These minimally invasive procedures can diagnose and treat conditions such as endometriosis, fibroids, and blockages in the fallopian tubes.
- Varicocele Repair: Surgical correction of varicoceles in men can improve sperm quality.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
- Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): This procedure involves placing washed and concentrated sperm directly into the uterus around the time of ovulation.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a process where eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a lab. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): This is a specialized form of IVF where a single sperm is injected directly into an egg to facilitate fertilization, often used in cases of severe male infertility.
- Donor Eggs or Sperm: In cases where one partner’s gametes are not viable, donor eggs or sperm can be used.
- Surrogacy: When a woman cannot carry a pregnancy to term, another woman (a surrogate) can carry the pregnancy using the couple’s embryos.
Lifestyle and Complementary Therapies
- Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight, balanced diet, and regular exercise can improve fertility in both men and women.
- Stress Reduction: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and acupuncture may help reduce stress and improve fertility outcomes.
- Avoiding Toxins: Reducing exposure to environmental toxins, quitting smoking, and limiting alcohol and caffeine intake can positively impact fertility.
Coping with Infertility
Dealing with infertility can be emotionally taxing. It’s important for couples to seek support and consider the following strategies:
- Counseling: Professional counseling can help individuals and couples cope with the emotional aspects of infertility.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups can provide a sense of community and shared experience.
- Open Communication: Maintaining open and honest communication with your partner is crucial for emotional support.
- Education: Learning about infertility and its treatments can empower couples to make informed decisions.
Infertility is a complex condition with numerous potential causes and treatments. Advances in medical science have provided many options for couples struggling to conceive. While the journey can be challenging, understanding the underlying causes and available treatments can offer hope and direction. It’s essential for couples to seek professional medical advice and support as they navigate this journey towards building their family. Click here for more information