How to Deal with Insomnia: Comprehensive Strategies for Better Sleep
Introduction

Insomnia, a common sleep disorder, affects millions of people worldwide, leading to struggling in falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. This can result in poor sleep quality, affecting daily functioning and overall health. Understanding the underlying causes and implementing effective strategies is crucial for managing and overcoming insomnia. In this article, we will take a look at various approaches to help you deal with insomnia and achieve better sleep.
Understanding Insomnia
Types of Insomnia
- Acute Insomnia: Short-term insomnia often triggered by stress, significant life changes, or trauma. It usually lasts for a few days or weeks.
- Chronic Insomnia: Long-term insomnia that persists for a month or longer. It may be associated with underlying medical conditions, medications, or psychological issues.
Common Causes of Insomnia

- Stress and Anxiety: Worries about work, health, or finances can keep your mind active at night.
- Poor Sleep Habits: Irregular sleep schedules, using electronic devices before bed, and consuming caffeine or alcohol can disrupt sleep patterns.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic pain, asthma, allergies, and other health issues can interfere with sleep.
- Medications: Some medications for asthma, depression, or high blood pressure can cause insomnia.
- Environmental Factors: Noise, light, and uncomfortable temperatures can make it difficult to sleep.
Lifestyle Changes for Better Sleep
- Establish a Sleep Routine: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading, taking a warm bath, or practicing relaxation techniques.
- Limit Exposure to Screens: Avoid screens from TVs, computers, and smartphones at least an hour before bed. The blue light emitted can interfere with melatonin production.
- Watch What You Eat and Drink: Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime. Opt for a light snack if you’re hungry.
- Exercise Regularly: Regular physical activity can help you fall asleep faster and enjoy deeper sleep. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days, but avoid robust exercise close to bedtime.
- Create a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is conducive to sleep by keeping it cool, dark, and quiet. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)
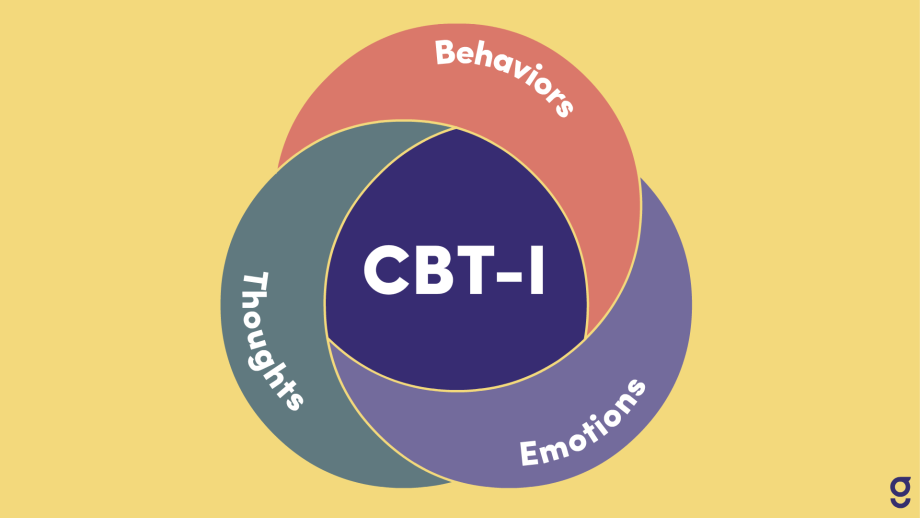
CBT-I is a structured program that helps identify and replace thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen sleep problems with habits that promote sound sleep. It involves:
- Sleep Restriction: Limiting the amount of time spent in bed to increase sleep efficiency. This involves gradually increasing the time allowed for sleep as sleep improves.
- Stimulus Control: Associating the bed with sleep by using it only for sleep and sex, and getting out of bed if unable to sleep within 20 minutes.
- Sleep Hygiene Education: Learning about practices that promote better sleep, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a bedtime routine.
- Cognitive Restructuring: Identifying and challenging negative thoughts about sleep, and replacing them with positive, realistic ones.
- Relaxation Techniques: Incorporating methods such as progressive muscle relaxation, deep breathing, and visualization to reduce anxiety and promote sleep.
Medical Treatments
If lifestyle changes and CBT-I are not effective, medical treatments may be necessary. These include:
- Medications: Prescription sleep aids or over-the-counter options may be recommended for short-term use. It’s important to use these under the guidance of a healthcare provider to avoid dependency and side effects.
- Supplements: Melatonin supplements can be beneficial for some people. Consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplement.
- Addressing Underlying Conditions: Treating conditions like chronic pain, depression, or anxiety can improve sleep. This may involve working with a specialist or utilizing specific therapies.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
- Herbal Remedies: Some people find relief with herbal supplements like valerian root, chamomile, or lavender. Always discuss with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
- Acupuncture: This traditional Chinese medicine practice may help improve sleep by balancing the body’s energy flow.
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices such as mindfulness meditation, guided imagery, and yoga can reduce stress and promote relaxation, aiding in better sleep.
When to Seek Professional Help
If insomnia persists despite making lifestyle changes and trying various self-help strategies, it may be time to seek professional help. Consult a healthcare provider if you:
- Have persistent difficulty falling or staying asleep.
- Experience daytime fatigue, mood changes, or difficulty concentrating.
- Suspect an underlying health condition contributing to your sleep problems.
- Rely on sleep aids several times a week.
Dealing with insomnia requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes, cognitive behavioral therapy, medical treatments, and possibly complementary therapies. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing effective strategies, you can improve your sleep quality and overall well-being. Remember, it’s important to be patient and consistent with these approaches, as achieving better sleep may take time. If insomnia continues to affect your daily life, seeking professional help is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
