The Impact of Sugar on Health
Introduction

Sugar, a ever-present ingredient in modern diets, plays an important role in our food choices and health outcomes. While it is a source of quick energy and adds flavor to food, immoderate sugar consumption is linked to numerous health issues. This article dives into the various effects of sugar on health, the types of sugar, and strategies for reducing intake to promote better overall well-being.
Types of Sugar
To understand the impact of sugar on health, it’s necessary to distinguish between different types of sugar:
- Natural Sugars: These sugars are found naturally in foods such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. They include fructose in fruits and lactose in dairy.
- Added Sugars: These sugars are added to foods and beverages during processing or preparation. Common examples include sucrose (table sugar), high-fructose corn syrup, and honey.
The Impact of Sugar on Health
- Weight Gain and Obesity

One of the most notable impacts of excessive sugar intake is weight gain. Sugary foods and drinks are often high in calories but low in nutritional value, leading to an increase in overall caloric intake. This can contribute to weight gain and, over time, obesity. Obesity is a risk factor for numerous health conditions, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
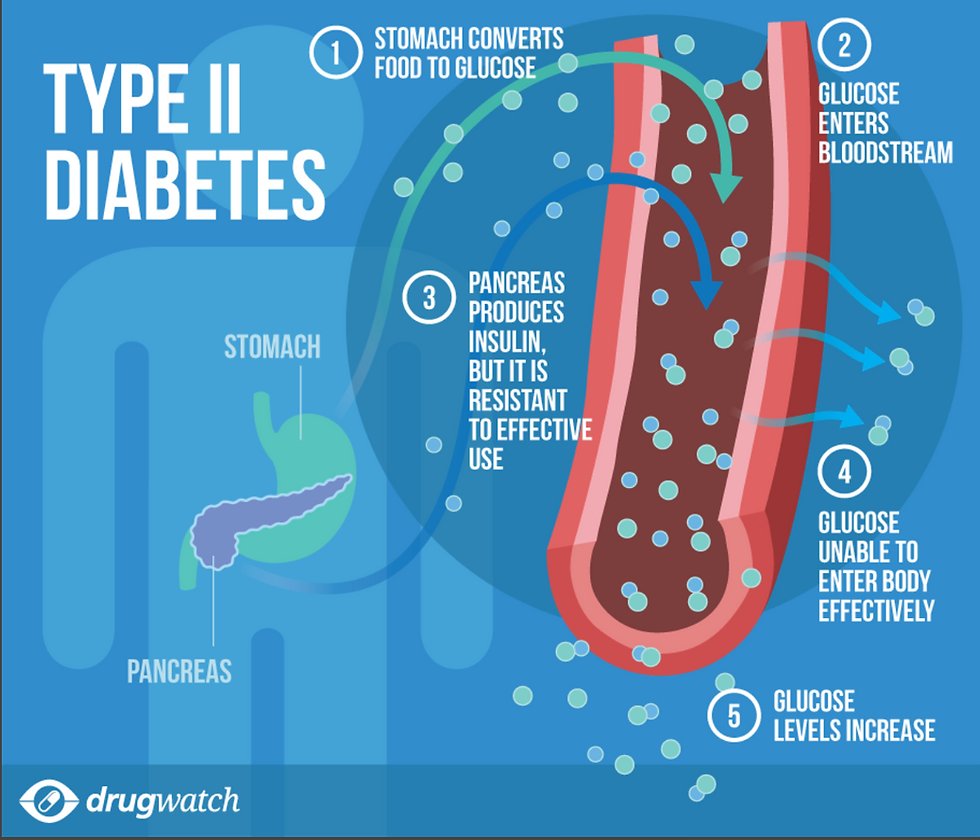
Consistently high sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, where the body’s cells become less responsive to insulin. This can eventually result in type 2 diabetes, a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. Managing diabetes requires careful monitoring of sugar intake and overall diet.
3. Heart Disease

Excessive sugar consumption is linked to an increased risk of heart disease. High sugar diets can lead to inflammation, high blood pressure, and elevated triglyceride levels, all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Additionally, sugar can contribute to obesity, further increasing the risk of heart problems.
4. Dental Health
Sugar is a primary contributor to tooth decay. When bacteria in the mouth metabolize sugar, they produce acids that erode tooth enamel, leading to cavities. Maintaining good oral hygiene and reducing sugar intake are crucial for dental health.
5. Liver Health
High fructose consumption, particularly from sugary beverages, can overload the liver. The liver metabolizes fructose, and excessive amounts can lead to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition where fat builds up in the liver, potentially leading to liver inflammation and damage.
6. Mental Health

Emerging research suggests a link between high sugar intake and mental health issues such as depression and anxiety. Sugar can cause spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, leading to mood swings and fatigue. Long-term high sugar consumption may also affect brain function and cognitive health.
7. Skin Health.

Diets high in sugar may accelerate skin aging and contribute to acne. Sugar can increase inflammation and the production of certain hormones, exacerbating skin conditions. Reducing sugar intake may improve skin clarity and overall appearance.
Strategies for Reducing Sugar Intake
Reducing sugar intake is vital for maintaining good health. Here are some practical strategies:
- Read Food Labels: Pay attention to food labels to identify added sugars. Look for ingredients such as sucrose, high-fructose corn syrup, and other syrups. Be aware of “hidden” sugars in products marketed as healthy, like granola bars and flavored yogurts.
- Choose Natural Sweeteners: Opt for natural sweeteners like stevia, monk fruit, or small amounts of honey or maple syrup. These alternatives can satisfy your sweet tooth with fewer negative health impacts.
- Limit Sugary Beverages: Reduce consumption of sodas, energy drinks, and sweetened teas. Instead, choose water, herbal teas, or sparkling water with a splash of natural juice.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the ingredients and reduce added sugars. Experiment with recipes that use whole foods and natural flavors.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce sugar cravings. Fiber slows the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, promoting better blood sugar control.
- Eat Balanced Meals: Include a balance of proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates in your meals. This combination helps stabilize blood sugar levels and reduces the likelihood of sugar cravings.
- Stay Hydrated: Sometimes thirst is mistaken for hunger or sugar cravings. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay hydrated and reduce the temptation to reach for sugary snacks.
- Mindful Eating: Practice mindful eating by paying attention to hunger and fullness cues. Avoid eating out of boredom or stress, and savor the flavors of whole, unprocessed foods.
While sugar can enhance the taste of foods and provide a quick energy boost, its excessive consumption poses significant health risks. From weight gain and diabetes to heart disease and mental health issues, the impact of sugar on health is profound. By understanding the types of sugar and adopting strategies to reduce intake, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health and well-being. Prioritizing whole foods, reading labels, and making mindful choices are essential components of a healthier diet with reduced sugar consumption.
