The Dangers of Smoking and How to Quit
Smoking is a global health crisis, responsible for millions of deaths each year. Despite the firmly established risks, millions of people continue to smoke even more. This article dives into the dangers of smoking, its impact on health, and effective strategies for quitting.
The Health Risks of Smoking
1. Cardiovascular Diseases
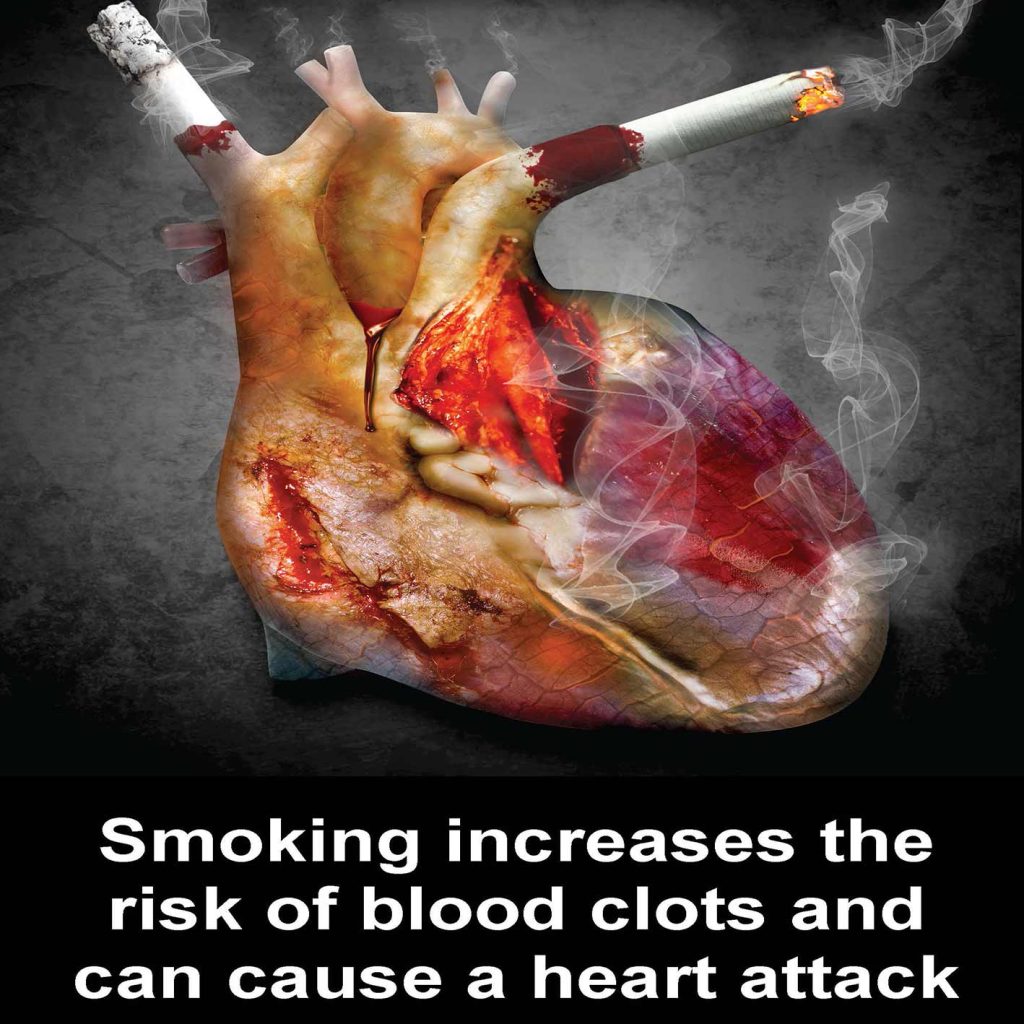
Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (CVD), including coronary heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lining of blood vessels, increase the build-up of plaque in arteries, and raise blood pressure and heart rate, leading to an increased risk of heart attacks and strokes. Smoking is a major cause of cardiovascular diseases CVD and is responsible for one in ever four deaths from CVD. Secondhand smoke exposure causes heart disease and stroke. Quitting smoking can protect people from cardiovascular disease and death.
2. Respiratory Diseases
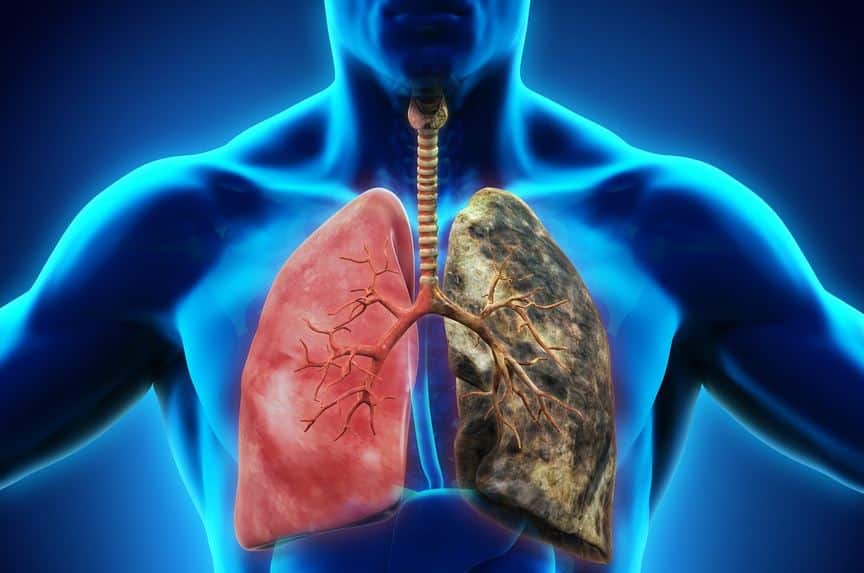
Smoking is the leading cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. It also exacerbates asthma and other respiratory conditions. The smoke irritates the airways, causing inflammation and narrowing, which leads to difficulty in breathing and reduced lung function.
3. Cancer
Smoking is linked to various types of cancer, most notably lung cancer, which is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Other cancers associated with smoking include mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreas, bladder, kidney, liver, stomach, cervix, and even some forms of leukemia. The carcinogens in tobacco smoke damage the DNA in cells, leading to mutations and the uncontrolled cell growth characteristic of cancer.
4. Reproductive Health Issues
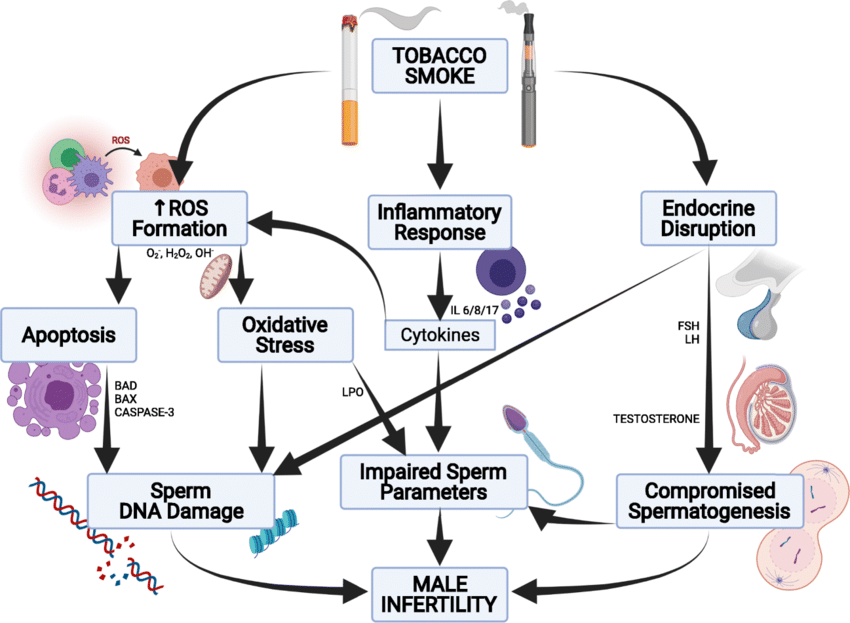
In men, smoking can lead to erectile dysfunction by damaging blood vessels and reducing blood flow. In women, smoking is linked to reduced fertility, complications during pregnancy, premature birth, low birth weight, and an increased risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Smoking also affects hormone levels, which can cause menstrual cycle irregularities.
5. Weakened Immune System
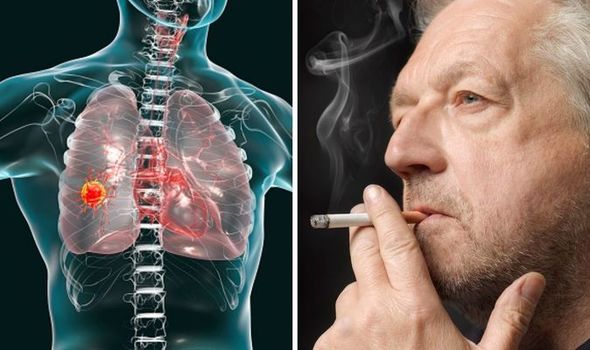
Smoking weakens the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and diseases. Smokers are more prone to respiratory infections like pneumonia and influenza, and the recovery time from illnesses is longer compared to non-smokers.
6. Impact on Oral Health
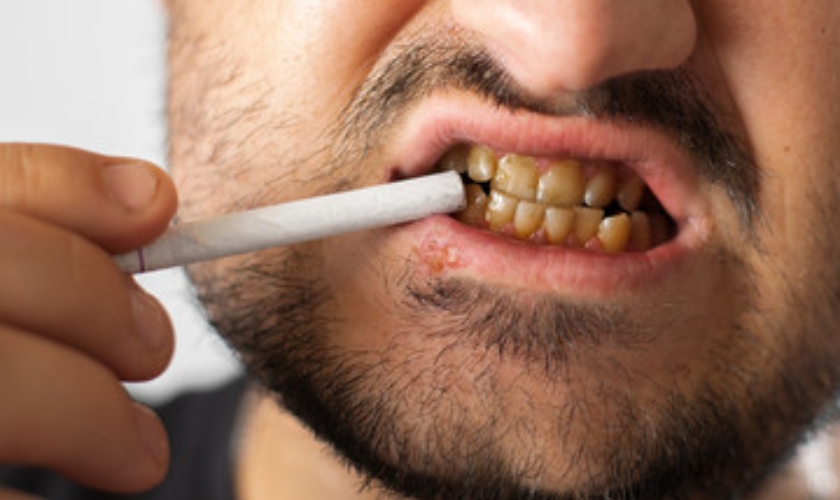
Smoking has damaging effects on oral health, leading to bad breath, stained teeth, gum disease, and tooth loss. It also increases the risk of oral cancers. The chemicals in tobacco smoke reduce blood flow to the gums, making them more susceptible to infections. smoking decreases your gum’s blood flow and deprives them of nutrients and oxygen that allows your gum to maintain their health.
The Financial and Social Costs of Smoking
Smoking is not only a health hazard but also a financial burden. The cost of purchasing cigarettes, combined with the healthcare expenses associated with treating smoking-related diseases, adds up significantly. Additionally, smoking can lead to lost productivity due to illness and premature death.
Socially, smoking can affect relationships and social interactions. The smell of smoke, the need to take smoking breaks, and the stigma associated with smoking can isolate smokers from non-smokers. Moreover, smoking in the home exposes family members, especially children, to secondhand smoke, which has its own health risks.
The Benefits of Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking has immediate and long-term health benefits. Within minutes to hours after the last cigarette, the body begins to repair itself. Blood pressure and heart rate normalize, carbon monoxide levels in the blood drop, and oxygen levels increase. Within weeks to months, lung function improves, and the risk of heart attack decreases. Over time, the risks of stroke, cancer, and other smoking-related diseases significantly decline.
Effective Strategies for Quitting Smoking
1. Prepare for the Quit Day
Choosing a quit day and preparing for it is crucial. Inform family and friends about your decision, remove cigarettes and smoking-related items from your environment, and plan how to handle triggers and cravings.
2. Seek Professional Help
Healthcare providers can offer guidance and support for quitting smoking. They can recommend nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs) like patches, gum, lozenges, inhalers, or nasal sprays, which help reduce withdrawal symptoms by providing a controlled dose of nicotine without the harmful chemicals found in cigarettes.
3. Consider Prescription Medications
Medications like varenicline (Chantix) and bupropion (Zyban) can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. These medications should be used under the supervision of a healthcare provider.
4. Behavioral Therapy
Working with a counselor or joining a support group can provide emotional support and coping strategies. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) helps identify and change the thought patterns and behaviors associated with smoking.
5. Mobile Apps and Online Resources
There are numerous mobile apps and online resources designed to support individuals in their journey to quit smoking. These tools offer tips, tracking systems, motivational messages, and community support.
6. Stay Active
Physical activity can help reduce cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Exercise releases endorphins, which improve mood and reduce stress. Finding a physical activity you enjoy can also serve as a distraction from the urge to smoke.
7. Adopt Healthy Eating Habits
Maintaining a healthy diet can help manage weight gain that some people experience when they quit smoking. Eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can improve overall health and energy levels.
8. Stay Hydrated
Drinking water can help flush nicotine and other toxins from the body. It also keeps the hands and mouth busy, which can help reduce the urge to smoke.
9. Avoid Triggers
Identify and avoid situations, people, or activities that trigger the urge to smoke. This might mean avoiding certain social settings, changing your routine, or finding new ways to cope with stress.
10. Practice Relaxation Techniques
Stress is a common trigger for smoking. Practicing relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation can help manage stress without the need for cigarettes.
Quitting smoking is one of the best decisions you can make for your health. The journey to becoming smoke-free can be challenging, but the benefits far outweigh the awkwardness. With the right strategies and support, you can overcome the addiction and enjoy a healthier, longer life. Remember, it’s never too late to quit smoking and start reaping the rewards of a smoke-free life.
