The Importance of Hydration: Why Staying Hydrated is Crucial for Your Health

Introduction: Staying hydrated essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Water is important for many of the body’s functions, including temperature regulation, joint lubrication, and the transportation of nutrients. Despite its importance, many people do not drink up enough water daily. This article will investigate the role of water in the body, the effects of dehydration, and practical tips for staying hydrated.
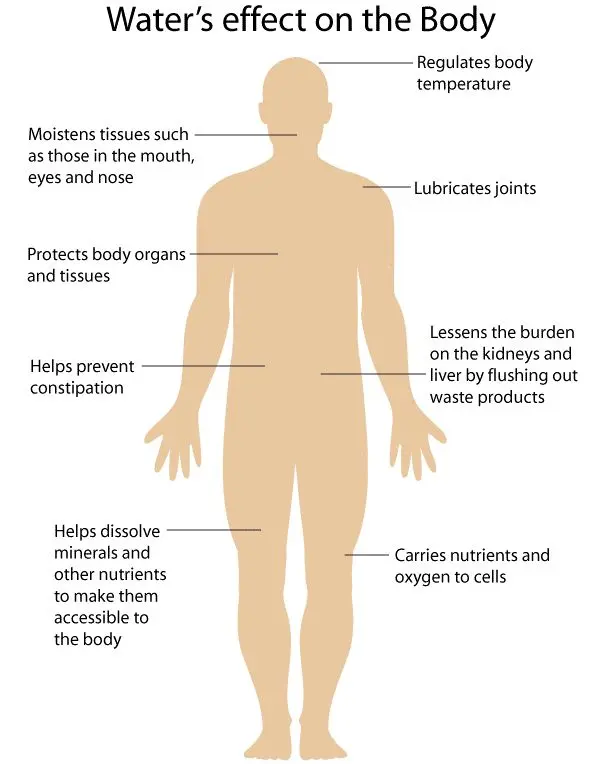
The Role of Water in the Body
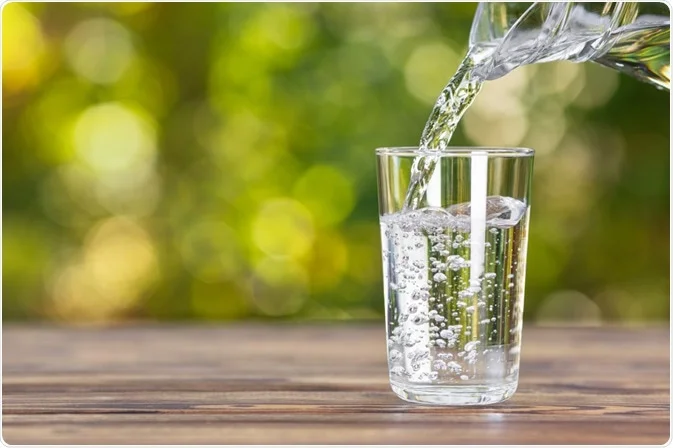

Water is a basic component of the human body, making up about 60% of body weight. It plays several critical roles, including:
- Regulating Body Temperature:
- Water helps dissolves heat through sweating and respiration, keeping the body cool and preventing overheating.
- Lubricating Joints:
- Synovial fluid, which lubricates and cushions the joints, is primarily composed of water. Proper hydration ensures that joints remain supple and function smoothly.
- Transporting Nutrients and Oxygen:
- Water is a key component of blood, which transports nutrients, oxygen, and waste products to and from cells.
- Aiding Digestion:
- Water is necessary for the digestion and absorption of food. It helps break down food particles and facilitates nutrient absorption in the intestines.
- Maintaining Skin Health:
- Adequate hydration helps maintain skin elasticity and moisture, contributing to a healthy complexion and preventing dryness.
- Supporting Cellular Functions:
- Every cell in the body requires water to function properly. Water is involved in various biochemical reactions and is essential for cellular processes.
Effects of Dehydration
Dehydration occurs when the body loses more water than it takes in. Even mild dehydration can have significant effects on health and well-being. Some common symptoms and consequences of dehydration include:
- Fatigue and Low Energy Levels:
- Dehydration can lead to a decrease in blood volume, causing the heart to work harder to pump blood. This can result in feelings of fatigue and low energy.
- Impaired Cognitive Function:
- Dehydration can affect cognitive functions such as concentration, alertness, and short-term memory. Studies have shown that even mild dehydration can impair cognitive performance.
- Headaches and Dizziness:
- A lack of adequate hydration can cause headaches and dizziness due to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain.
- Digestive Issues:
- Dehydration can lead to constipation and other digestive problems as the body absorbs more water from the intestines, making stool harder and more difficult to pass.
- Kidney Problems:
- Chronic dehydration can contribute to the development of kidney stones and urinary tract infections, as concentrated urine creates an environment for stone formation and bacterial growth.
- Skin Issues:
- Dehydrated skin can become dry, tight, and flaky. Long-term dehydration can contribute to the development of wrinkles and other signs of aging.
Tips for Staying Hydrated
Maintaining proper hydration is essential for overall health. Here are some practical tips to help you stay hydrated throughout the day:
- Drink Plenty of Water:
- Aim to drink at least eight 8-ounce glasses of water per day, known as the “8×8” rule. However, individual water needs can vary based on factors such as age, weight, activity level, and climate.
- Consume Hydrating Foods:
- Include water-rich foods in your diet, such as fruits (watermelon, oranges, strawberries) and vegetables (cucumbers, lettuce, celery).
- Carry a Water Bottle:
- Keep a reusable water bottle with you throughout the day to remind you to drink water regularly. Sipping water consistently can help you stay hydrated.
- Set Reminders:
- Use smartphone apps or set alarms to remind you to drink water at regular intervals, especially if you tend to forget to hydrate during busy periods.
- Monitor Urine Color:
- Pay attention to the color of your urine. Pale yellow urine typically indicates proper hydration, while dark yellow or amber urine may be a sign that you need to drink more water.
- Hydrate Before, During, and After Exercise:
- Drink water before, during, and after physical activity to replenish fluids lost through sweat. This is particularly important during intense or prolonged exercise.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol:
- Both caffeine and alcohol can have diuretic effects, leading to increased urine production and potential dehydration. Consume these beverages in moderation and balance them with water intake.
- Drink Herbal Teas:
- Herbal teas can be a hydrating alternative to water. Choose caffeine-free options like chamomile, mint, or rooibos for added hydration.
Special Considerations
Certain groups of people may have increased hydration needs or face specific challenges in maintaining proper hydration:
- Athletes and Active Individuals:
- Those who engage in regular physical activity or intense exercise may require additional fluids to compensate for sweat loss. Sports drinks containing electrolytes can be beneficial during prolonged exercise.
- Elderly Adults:
- Older adults may have a reduced sense of thirst and may be more prone to dehydration. It is important for caregivers to encourage regular fluid intake for the elderly.
- Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women:
- Hydration needs increase during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Pregnant women should aim to drink at least 10 cups of fluids per day, and breastfeeding women should consume an additional 3-4 cups.
- Children:
- Children may not always recognize when they are thirsty. Parents and caregivers should encourage regular water breaks, especially during play and physical activities.
Hydration is a cornerstone of good health. Water is important for many of the body’s vital functions, and staying properly hydrated can prevent a range of health issues. By understanding the importance of hydration and adopting practical strategies to maintain adequate fluid intake, you can support your overall health and well-being. Make hydration a priority in your daily routine, and reap the benefits of a well-hydrated body.
