Understanding Diabetes: A Comprehensive Guide to Prevention, Management, and Care

Introduction
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Characterized by elevated blood glucose levels, diabetes can lead to severe health complications if not properly managed. Understanding diabetes, its types, risk factors, prevention strategies, and management techniques is crucial for maintaining a healthy life. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a detailed overview of diabetes, offering valuable insights and practical advice for prevention, management, and care.
Types of Diabetes
There are three major types of diabetes: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Each type has distinct attributes and requires specific management strategies.
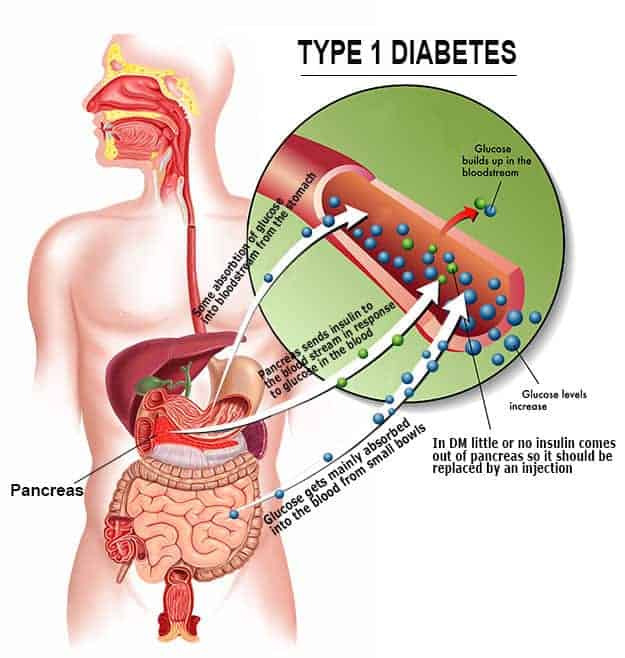
- An autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas.
- Typically diagnosed in children and young adults.
- Requires lifelong insulin therapy
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
- The most common form of diabetes, often associated with obesity and a sedentary lifestyle.
- Characterized by insulin resistance and eventual insulin deficiency.
- Can be managed with lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin.
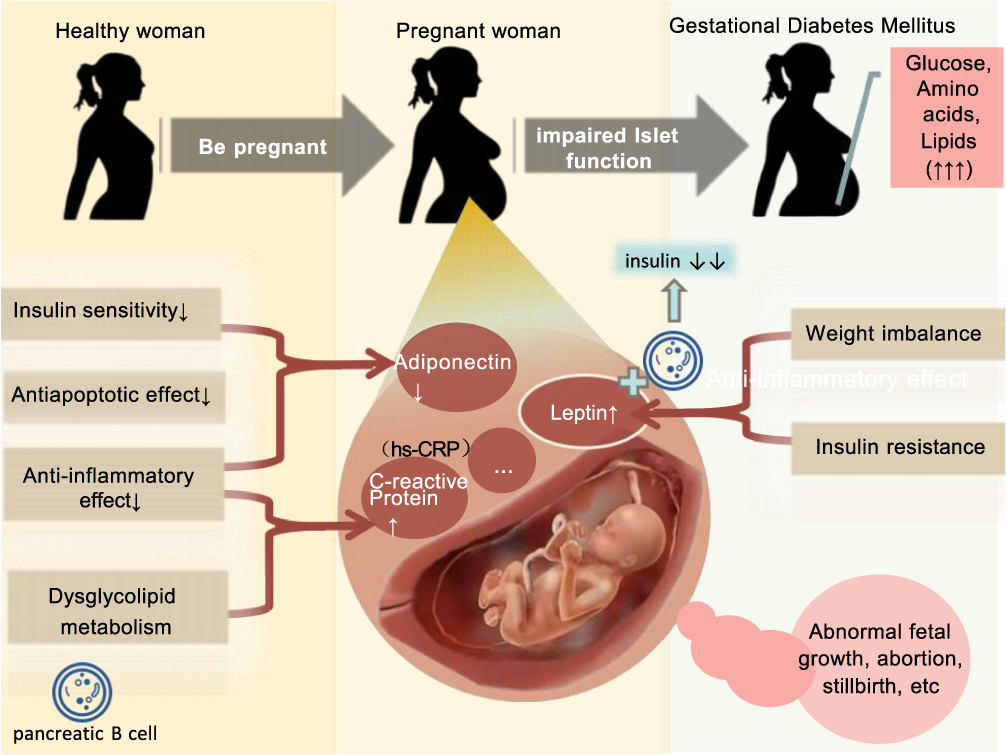
- Occurs during pregnancy when the body cannot produce enough insulin to meet increased needs.
- Typically resolves after childbirth but increases the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Gestational diabetes is diabetes diagnosed for the first time. Like other types of diabetes, gestational diabetes affects how your cells use sugar (glucose). Gestational diabetes causes high blood sugar that can affect your pregnancy and your baby’s health.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Several risk factors contribute to the development of diabetes, including genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
- Genetic Factors:
- Family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- Certain ethnic groups (e.g., African American, Hispanic, Native American, and Asian American) have a higher prevalence.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Poor diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats.
- Lack of physical activity and sedentary lifestyle.
- Excessive alcohol consumption and smoking.
- Health Conditions:
- Obesity and overweight.
- High blood pressure and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
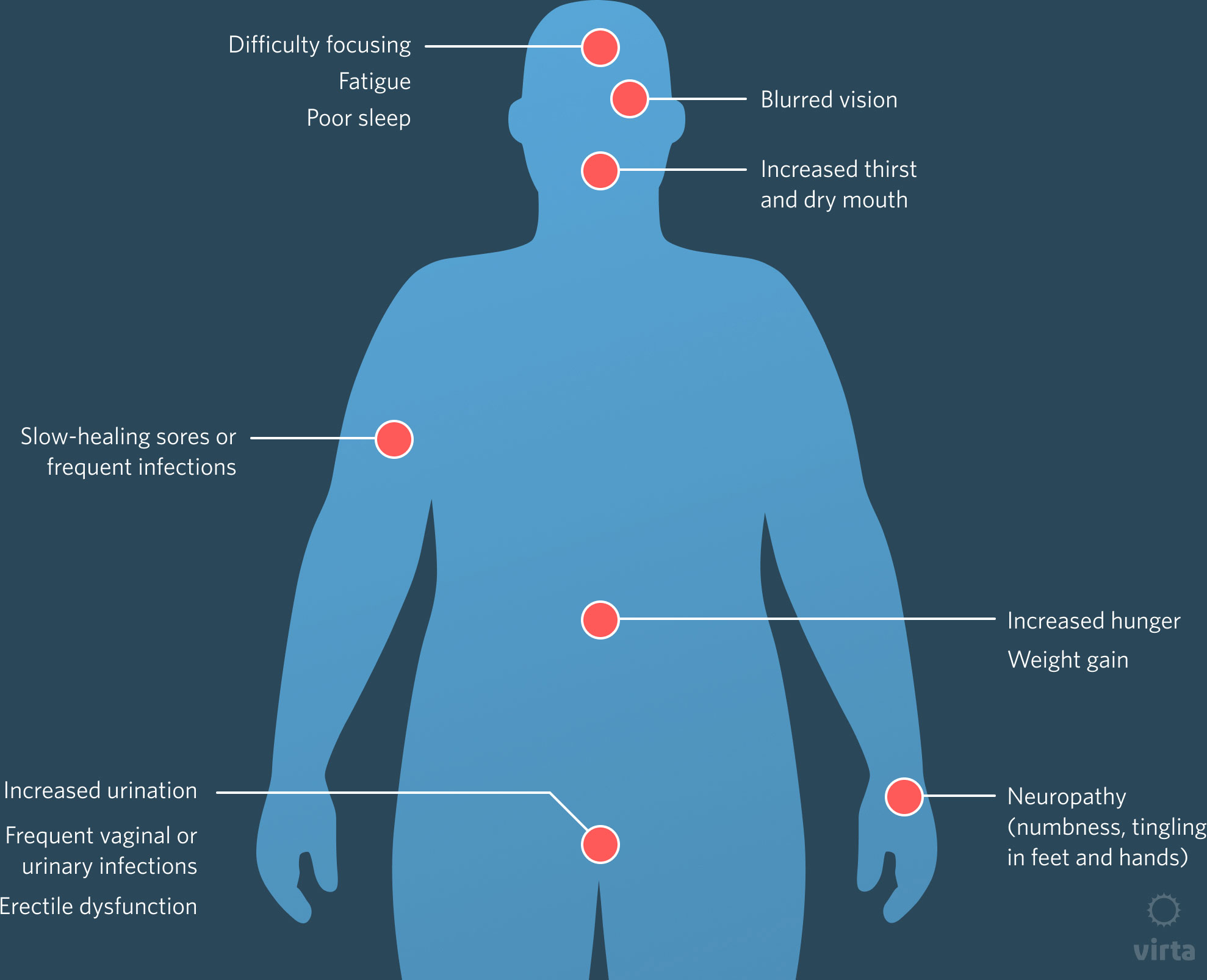
Recognizing the symptoms of diabetes is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Frequent Urination: High blood glucose levels cause excess glucose to be excreted in the urine.
- Increased Thirst: Dehydration from frequent urination leads to excessive thirst.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: The body breaks down fat and muscle for energy due to insufficient insulin.
- Fatigue: Lack of glucose in cells leads to reduced energy levels.
- Blurred Vision: High blood sugar can cause swelling in the lens of the eye.
- Slow Healing: Cuts and wounds heal slowly due to impaired blood flow and immune response.
Diagnosis is typically confirmed through blood tests. The process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from it’s signs and seasons. A health history, physical exam, and tests, such as blood tests, imaging tests, and biopsies, may be used to help make a diagnosis.
- Fasting Blood Glucose Test: Measures blood sugar levels after an overnight fast.
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): Measures blood sugar levels before and after consuming a sugary drink.
- Hemoglobin A1c Test: Reflects average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing diabetes, especially Type 2 diabetes, involves adopting a healthy lifestyle. Here are some effective strategies:
- Healthy Diet:
- Focus on whole foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Limit intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-fat foods.
- Monitor portion sizes and practice mindful eating.
- Regular Physical Activity:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
- Include strength training exercises at least twice a week.
- Incorporate physical activity into daily routines, such as walking or biking to work.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight through diet and exercise.
- Even modest weight loss (5-7% of body weight) can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes.
- Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol:
- Avoid smoking, as it increases the risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly, especially if you have risk factors for diabetes.
- Get regular screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol, and other related health conditions.
Managing Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and regular monitoring.
- Blood Glucose Monitoring:
- Regularly check blood sugar levels using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
- Keep track of blood sugar readings to identify patterns and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Medication:
- Type 1 diabetes requires lifelong insulin therapy.
- Type 2 diabetes can be managed with oral medications, non-insulin injectables, and sometimes insulin.
- Medications help regulate blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce glucose production in the liver.
- Healthy Eating:
- Follow a balanced diet tailored to individual needs and preferences.
- Count carbohydrates to manage blood sugar levels effectively.
- Work with a registered dietitian or diabetes educator to create a personalized meal plan.
- Physical Activity:
- Engage in regular physical activity to improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels.
- Include a mix of aerobic, strength training, and flexibility exercises.
- Monitor blood sugar levels before and after exercise to prevent hypoglycemia.
- Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels and overall health.
- Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises.
- Ensure adequate sleep and relaxation to support mental and physical well-being.
- Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Schedule regular visits with healthcare providers to monitor diabetes and related health conditions.
- Get routine screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol, kidney function, and eye health.
- Collaborate with a diabetes care team, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators.
Complications of Diabetes
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to severe complications affecting various organs and systems in the body:
- Cardiovascular Disease:
- Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and peripheral artery disease.
- High blood sugar levels damage blood vessels and nerves controlling the heart.
- Kidney Damage (Nephropathy):
- High blood sugar levels damage the kidneys’ filtering system.
- Can lead to chronic kidney disease and eventual kidney failure.
- Nerve Damage (Neuropathy):
- High blood sugar levels damage nerves, leading to pain, tingling, and numbness in extremities.
- Can cause digestive issues, sexual dysfunction, and other problems.
- Eye Damage (Retinopathy):
- Damage to blood vessels in the retina can lead to vision problems and blindness.
- Increased risk of cataracts and glaucoma.
- Foot Problems:
- Nerve damage and poor blood flow increase the risk of foot ulcers and infections.
- Severe cases may require amputation.
- Skin Conditions:
- Increased risk of bacterial and fungal infections.
- Slow healing of cuts and wounds.
Living with Diabetes
Living with diabetes requires ongoing management and adaptation. Here are some tips for thriving with diabetes:
- Education and Support:
- Learn about diabetes, its management, and potential complications.
- Join diabetes support groups or online communities for encouragement and advice.
- Work closely with healthcare providers to create and adjust your diabetes management plan.
- Daily Routine:
- Establish a daily routine that includes regular meals, physical activity, and medication.
- Monitor blood sugar levels consistently and adjust activities and meals as needed.
- Technology and Tools:
- Use diabetes management apps and tools to track blood sugar levels, diet, and physical activity.
- Consider using continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) for real-time blood sugar tracking.
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Prioritize a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
- Maintain regular health check-ups and screenings.
- Emergency Preparedness:
- Carry a diabetes emergency kit with glucose tablets, insulin, and medical identification.
- Educate family and friends about diabetes management and emergency procedures.
Understanding diabetes and its impact is essential for effective prevention, management, and care. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar levels, and working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while minimizing the risk of complications. Continuous education, support, and proactive health management are key to thriving with diabetes and maintaining overall well-being. Remember, small changes can make a significant difference in managing diabetes and improving quality of life.
I hope this comprehensive article meets your needs for your blog! Let me know if there are any specific aspects you’d like to expand or adjust
